Overview
Over pronation is when there is excessive or too much movement of the foot. Over pronation is a very common cause of heel pain and general pain throughout the lower extremities. This condition can often be referred to as flat feet and causes you to walk on other parts of your foot, which is what leads to serious heel and foot pain.
Causes
There are many possible causes for overpronation, but researchers have not yet determined one underlying cause. Hintermann states, Compensatory overpronation may occur for anatomical reasons, such as a tibia vara of 10 degrees or more, forefoot varus, leg length discrepancy, ligamentous laxity, or because of muscular weakness or tightness in the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles. Pronation can be influenced by sources outside of the body as well. Shoes have been shown to significantly influence pronation. Hintermann states that the same person can have different amounts of pronation just by using different running shoes. It is easily possible that the maximal ankle joint eversion movement is 31 degrees for one and 12 degrees for another running shoe.
Symptoms
It is important to note that pronation is not wrong or bad for you. In fact, our feet need to pronate and supinate to achieve proper gait. Pronation (rolling inwards) absorbs shock and supination (rolling outwards) propels our feet forward. It is our body?s natural shock-absorbing mechanism. The problem is over-pronation i.e. the pronation movement goes too deep and lasts for too long, which hinders the foot from recovering and supinating. With every step, excess pronation impedes your natural walking pattern, causing an imbalance in the body and consequent excessive wear and tear in joints, muscles and ligaments. Some common complaints associated with over-pronation include Heel Pain (Plantar Fasciitis) ,Ball of foot pain, Achilles Tendonitis, Shin splints, Knee Pain, Lower Back Pain.
Diagnosis
Look at the wear on your shoes and especially running trainers; if you overpronate it's likely the inside of your shoe will be worn down (or seem crushed if they're soft shoes) from the extra strain.
Non Surgical Treatment
Supportive orthotics in the shoe is a method commonly implemented to treat many common running injuries associated with pronation. An advantage of orthotics is that they often allow the sufferer to continue to participate in athletic activity and avoid other treatment options that could be potentially costly and time consuming. Seventy-five percent of injured runners are successfully treated with the prescription of orthoses. Orthotics are the most effective treatment for symptoms that develop from unusual biomechanics within the body such as overpronation, resulting in either great improvement or complete healing of the injury in about half the cases.
Prevention
Many of the prevention methods for overpronation-orthotics, for example-can be used interchangeably with treatment methods. If the overpronation is severe, you should seek medical attention from a podiatrist who can cast you for custom-made orthotics. Custom-made orthotics are more expensive, but they last longer and provide support, stability, and balance for the entire foot. You can also talk with a shoe specialist about running shoes that offer extra medial support and firm heel counters. Proper shoes can improve symptoms quickly and prevent them from recurring. Surgery can sometimes help cure and prevent this problem if you suffer from inherited or acquired pes planus deformity. Surgery typically involves stabilizing the bones to improve the foot?s support and function.
Over pronation is when there is excessive or too much movement of the foot. Over pronation is a very common cause of heel pain and general pain throughout the lower extremities. This condition can often be referred to as flat feet and causes you to walk on other parts of your foot, which is what leads to serious heel and foot pain.

Causes
There are many possible causes for overpronation, but researchers have not yet determined one underlying cause. Hintermann states, Compensatory overpronation may occur for anatomical reasons, such as a tibia vara of 10 degrees or more, forefoot varus, leg length discrepancy, ligamentous laxity, or because of muscular weakness or tightness in the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles. Pronation can be influenced by sources outside of the body as well. Shoes have been shown to significantly influence pronation. Hintermann states that the same person can have different amounts of pronation just by using different running shoes. It is easily possible that the maximal ankle joint eversion movement is 31 degrees for one and 12 degrees for another running shoe.
Symptoms
It is important to note that pronation is not wrong or bad for you. In fact, our feet need to pronate and supinate to achieve proper gait. Pronation (rolling inwards) absorbs shock and supination (rolling outwards) propels our feet forward. It is our body?s natural shock-absorbing mechanism. The problem is over-pronation i.e. the pronation movement goes too deep and lasts for too long, which hinders the foot from recovering and supinating. With every step, excess pronation impedes your natural walking pattern, causing an imbalance in the body and consequent excessive wear and tear in joints, muscles and ligaments. Some common complaints associated with over-pronation include Heel Pain (Plantar Fasciitis) ,Ball of foot pain, Achilles Tendonitis, Shin splints, Knee Pain, Lower Back Pain.
Diagnosis
Look at the wear on your shoes and especially running trainers; if you overpronate it's likely the inside of your shoe will be worn down (or seem crushed if they're soft shoes) from the extra strain.

Non Surgical Treatment
Supportive orthotics in the shoe is a method commonly implemented to treat many common running injuries associated with pronation. An advantage of orthotics is that they often allow the sufferer to continue to participate in athletic activity and avoid other treatment options that could be potentially costly and time consuming. Seventy-five percent of injured runners are successfully treated with the prescription of orthoses. Orthotics are the most effective treatment for symptoms that develop from unusual biomechanics within the body such as overpronation, resulting in either great improvement or complete healing of the injury in about half the cases.
Prevention
Many of the prevention methods for overpronation-orthotics, for example-can be used interchangeably with treatment methods. If the overpronation is severe, you should seek medical attention from a podiatrist who can cast you for custom-made orthotics. Custom-made orthotics are more expensive, but they last longer and provide support, stability, and balance for the entire foot. You can also talk with a shoe specialist about running shoes that offer extra medial support and firm heel counters. Proper shoes can improve symptoms quickly and prevent them from recurring. Surgery can sometimes help cure and prevent this problem if you suffer from inherited or acquired pes planus deformity. Surgery typically involves stabilizing the bones to improve the foot?s support and function.


 A rupture of the Achilles tendon means that there has been either a complete, or partial, tear of the tendon which connects the calf muscles to the heel bone. Usually this occurs just above insertion on the heel bone, although it can happen anywhere along the course of the tendon. Causes Your Achilles tendon helps you point your foot downward, rise on your toes and push off your foot as you walk. You rely on it virtually every time you move your foot. Rupture usually occurs in the section of the tendon located within 2 1/2 inches (about 6 centimeters) of the point where it attaches to the heel bone. This section may be predisposed to rupture because it gets less blood flow, which also may impair its ability to heal. Ruptures often are caused by a sudden increase in the amount of stress on your Achilles tendon. Common examples include increasing the intensity of sports participation, especially in sports that involve jumping, falling from a height, stepping into a hole. Symptoms A classic sign of an Achilles tendon rupture is the feeling of being hit in the Achilles are. There is often a "pop" sound. There may be little pain, but the person can not lift up onto his toes while weight bearing. Diagnosis The diagnosis of an Achilles tendon rupture can be made easily by an orthopedic surgeon. The defect in the tendon is easy to see and to palpate. No x-ray, MRI or other tests are necessary. Non Surgical Treatment Initial treatment for sprains and strains should occur as soon as possible. Remember RICE! Rest the injured part. Pain is the body's signal to not move an injury. Ice the injury. This will limit the swelling and help with the spasm. Compress the injured area. This again, limits the swelling. Be careful not to apply a wrap so tightly that it might act as a tourniquet and cut off the blood supply. Elevate the injured part. This lets gravity help reduce the swelling by allowing fluid and blood to drain downhill to the heart. Over-the-counter pain medication is an option. Acetaminophen (Tylenol) is helpful for pain, but ibuprofen (Motrin, Advil, Nuprin) might be better, because these medications relieve both pain and inflammation. Remember to follow the guidelines on the bottle for appropriate amounts of medicine, especially for children and teens.
A rupture of the Achilles tendon means that there has been either a complete, or partial, tear of the tendon which connects the calf muscles to the heel bone. Usually this occurs just above insertion on the heel bone, although it can happen anywhere along the course of the tendon. Causes Your Achilles tendon helps you point your foot downward, rise on your toes and push off your foot as you walk. You rely on it virtually every time you move your foot. Rupture usually occurs in the section of the tendon located within 2 1/2 inches (about 6 centimeters) of the point where it attaches to the heel bone. This section may be predisposed to rupture because it gets less blood flow, which also may impair its ability to heal. Ruptures often are caused by a sudden increase in the amount of stress on your Achilles tendon. Common examples include increasing the intensity of sports participation, especially in sports that involve jumping, falling from a height, stepping into a hole. Symptoms A classic sign of an Achilles tendon rupture is the feeling of being hit in the Achilles are. There is often a "pop" sound. There may be little pain, but the person can not lift up onto his toes while weight bearing. Diagnosis The diagnosis of an Achilles tendon rupture can be made easily by an orthopedic surgeon. The defect in the tendon is easy to see and to palpate. No x-ray, MRI or other tests are necessary. Non Surgical Treatment Initial treatment for sprains and strains should occur as soon as possible. Remember RICE! Rest the injured part. Pain is the body's signal to not move an injury. Ice the injury. This will limit the swelling and help with the spasm. Compress the injured area. This again, limits the swelling. Be careful not to apply a wrap so tightly that it might act as a tourniquet and cut off the blood supply. Elevate the injured part. This lets gravity help reduce the swelling by allowing fluid and blood to drain downhill to the heart. Over-the-counter pain medication is an option. Acetaminophen (Tylenol) is helpful for pain, but ibuprofen (Motrin, Advil, Nuprin) might be better, because these medications relieve both pain and inflammation. Remember to follow the guidelines on the bottle for appropriate amounts of medicine, especially for children and teens.  Surgical Treatment Surgical techniques for rupture repair are varied but usually involve reapproximation of the torn ends of the Achilles tendon, sometimes reinforced by the gastrocsoleus aponeurosis or plantaris tendon. Open reconstruction is undertaken using a medial longitudinal approach. Studies indicate that patients who undergo percutaneous, rather than an open, Achilles tendon rupture repair have a minimal rate of infection but a high rate of sural nerve entrapment (16.7% of treated cases). Prevention Good flexibility of the calf muscles plays an essential role in the prevention of Achilles tendon injuries. It is also important to include balance and stability work as part of the training programme. This should include work for the deep-seated abdominal muscles and for the muscles that control the hip. This might at first appear odd, given the fact that the Achilles are a good distance from these areas, but developing strength and control in this area (core stability) can boost control at the knee and ankle joints. Training errors should be avoided. The volume, intensity and frequency of training should be monitored carefully, and gradually progressed, particularly when introducing new modes of training to the programme. Abrupt changes in training load are the primary cause of Achilles tendinopathy.
Surgical Treatment Surgical techniques for rupture repair are varied but usually involve reapproximation of the torn ends of the Achilles tendon, sometimes reinforced by the gastrocsoleus aponeurosis or plantaris tendon. Open reconstruction is undertaken using a medial longitudinal approach. Studies indicate that patients who undergo percutaneous, rather than an open, Achilles tendon rupture repair have a minimal rate of infection but a high rate of sural nerve entrapment (16.7% of treated cases). Prevention Good flexibility of the calf muscles plays an essential role in the prevention of Achilles tendon injuries. It is also important to include balance and stability work as part of the training programme. This should include work for the deep-seated abdominal muscles and for the muscles that control the hip. This might at first appear odd, given the fact that the Achilles are a good distance from these areas, but developing strength and control in this area (core stability) can boost control at the knee and ankle joints. Training errors should be avoided. The volume, intensity and frequency of training should be monitored carefully, and gradually progressed, particularly when introducing new modes of training to the programme. Abrupt changes in training load are the primary cause of Achilles tendinopathy.
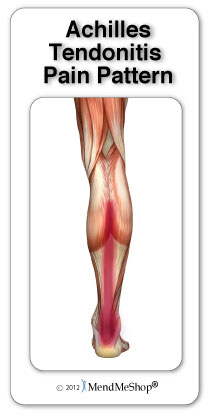 Do you experience dull pain near the back of your heel or in the back of your leg after your regular run or after playing your favourite sport? When you ramp up your exercise is the pain more severe or prolonged? If so, you may have Achilles tendinitis. The Achilles tendon is the thick, strong, springy band of tissue that connects the muscles from the middle of your calf to your heel bone. You use your Achilles tendon when you walk, run or jump. Achilles tendinitis occurs when the Achilles tendon is repeatedly strained. The Achilles tendon becomes less flexible, weaker and more prone to injury as we age. Middle-aged weekend warriors and runners who suddenly intensify their training often suffer from Achilles tendinitis.
Do you experience dull pain near the back of your heel or in the back of your leg after your regular run or after playing your favourite sport? When you ramp up your exercise is the pain more severe or prolonged? If so, you may have Achilles tendinitis. The Achilles tendon is the thick, strong, springy band of tissue that connects the muscles from the middle of your calf to your heel bone. You use your Achilles tendon when you walk, run or jump. Achilles tendinitis occurs when the Achilles tendon is repeatedly strained. The Achilles tendon becomes less flexible, weaker and more prone to injury as we age. Middle-aged weekend warriors and runners who suddenly intensify their training often suffer from Achilles tendinitis.




 The Achilles tendon is the extension from the two large muscles in the calf region, the gastrocnemius and the soleus. These two muscles combine to form the Achilles tendon. The tendon forms in the lower one third of the leg and extends to the back of the heel bone (calcaneus). When the muscles of the calf contract this produces tension on the Achilles tendon pulling on the back of heel causing the heel to rise and the foot to point downward. It is during this motion that high-tension force is transmitted through the Achilles tendon during pushing and jumping activity. This high tension force can cause the Achilles tendon to tear or rupture. This happens in 3 common locations. The most common location for a tendon tear is within the tendon substance just above the heel. The second and third most common locations are where the Achilles tendon attaches into the heel bone and higher in the leg, where the tendon begins.
The Achilles tendon is the extension from the two large muscles in the calf region, the gastrocnemius and the soleus. These two muscles combine to form the Achilles tendon. The tendon forms in the lower one third of the leg and extends to the back of the heel bone (calcaneus). When the muscles of the calf contract this produces tension on the Achilles tendon pulling on the back of heel causing the heel to rise and the foot to point downward. It is during this motion that high-tension force is transmitted through the Achilles tendon during pushing and jumping activity. This high tension force can cause the Achilles tendon to tear or rupture. This happens in 3 common locations. The most common location for a tendon tear is within the tendon substance just above the heel. The second and third most common locations are where the Achilles tendon attaches into the heel bone and higher in the leg, where the tendon begins.
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
